海洋拮抗菌研究的历史可追朔至19世纪,已有无数前人进行过海洋拮抗菌筛选的研究。Viju N等曾经报道过一株恶臭假单胞菌(Pseudomonas putida),发现其对细菌形成的生物膜均表现出很强的活性,并可以从中分离出潜在防污作用的化合物[4]。Perumal L等发现从孟加拉湾深海沉积物中分离到的海洋细菌具有广谱的抗菌活性和细胞毒性,并鉴定出拮抗海洋细菌为芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)、盐杆菌(Halobacillus)、葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus)和海洋杆菌(Marinobacter)[5]。Zhou S X等报道过Bacillus sp.YB1701对鱼类病原菌嗜水气单胞菌和副溶血弧菌具有抗菌作用,并可用于水产养殖有机废料的降解,是一种潜在的益生菌[6]。徐亚飞发现地衣芽孢杆菌(Baclicus lincheniformis )在生长代谢过程中能产生多种抗菌物质,这些物质对多种病原菌具有很强的拮抗作用[7]。
目前,已有很多学者研究了海洋共附生真菌的抗菌活性。Liu H等在海洋红藻细翼藻(Pterocladiella tenuis)内发现一株真菌(Penicillium chermesinum) EN-480的代谢产物,对条件致病菌黄体微球菌(Micrococcus luteus)具有一定的抑制活性[8]。Kuvarina A E等从嗜碱真菌(Emericellopsis basena) VKPM F1428中发现其产生的emericellipsin A(EmiA)具有很强的抗真菌和细胞毒作用[9]。Thiyagarajan S等从红树林和河口的沉积物中发现一株曲霉菌EF4对甲基球菌属(Methyloccus sp.)、黄杆菌属(Havobacterium sp.)、海洋球菌属(Marinococcus sp.)、沙雷氏菌属(Serratia sp.)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas sp.)均具有一定的抑制作用[10]。本研究以渔业养殖常见的革兰阴性致病菌作为指示病原菌,采用滤纸片扩散法研究海洋微生物的抑菌谱,旨在筛选出具有抗菌活性的海洋微生物,并探讨其作为益生菌,用于制作微生态制剂并应用于渔业养殖的可能性。
1 材料与方法
1.1 菌种
1.1.1 海洋分离微生物
由厦门医学院海洋药学研究中心提供的采集自福建东山兄弟屿的海绵、漳江口红树林的植株、土壤、螃蟹中分离提纯的74株海洋微生物(真菌71株、放线菌2株、细菌1株)。
1.1.2 测试病原菌
鳗鲡爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella anguillarum)A-01、A-02、A-03;迟缓爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella tarda)A-11、A-12、A-13;嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)E-01、E-02、E-03、E-04;维氏气单胞菌(Aeromonas veronii)E-11、E-12;副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahemolyticus)B-01、B-02、B-03、B-04、B-05、B-06、B-07、B-08;溶藻弧菌(Vibrio alginolyticus)B-11;哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)B-21;大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)C-01、C-02、C-03;鸡白痢沙门氏菌(Salmonella pullorum)D-01、D-02。均由集美大学水产学院提供,共9种27株。
1.2 主要试剂和培养基
诺氟沙星药物敏感纸片购自杭州微生物试剂有限公司。MH肉汤培养基(Mueller-hinton broth medium)购自青岛海博生物技术有限公司。胰酪胨大豆肉汤培养基(Trypticase soy broth medium,TSB)购自广东环凯微生物科技有限公司。LB肉汤培养基(LB broth medium)购自生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 指示病原菌的保存
将各类指示病原菌分别接种于含0.5 mL 20%甘油水溶液和1 mL对应培养液的冻存管中(每种菌株保存9管),按照4℃、-20℃、-80℃的顺序梯度保存。
1.3.2 样品菌菌体萃取物的制备
1.3.3 指示病原菌摇瓶制备
配制各指示病原菌对应培养液100 mL,分别加入对应指示病原菌冻存液200 μL,摇床培养24 h(32℃、200 r/min)。
1.3.4 抑菌谱的测定
采用Bauer和Kirby建立的圆纸片琼脂扩散法 (K-B法)对74株海洋菌株进行筛选[13]。将指示病原菌摇瓶培养液按照0.1%(V/V)的接种量,待培养液稍冷后接种于对应培养基中,充分摇匀后倒板。吸取5 μL样品菌菌体萃取物于6 mm滤纸圆片上,待培养基凝固后,贴于平板相应位置,以甲醇为阴性对照,以诺氟沙星药敏纸片为阳性对照,在32℃条件下,培养24 h。用直尺测量抑菌圈直径,每组设3个平行。
在7种指示病原菌中,气单胞菌采用LB培养基;沙门氏菌和大肠杆菌采用MH肉汤培养基;爱德华氏菌采用TSB培养基;副溶血弧菌、溶藻弧菌和哈维氏弧菌采用含2% NaCl的LB培养基。
抑菌圈敏感程度采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)和Tukey's多重比较进行统计分析,采用GraphPad Prism 9软件分析画图。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
1.3.5 最小抑菌浓度(MIC)药敏实验
采用微量肉汤稀释法测定芽孢杆菌N-14对维氏气单胞菌E-12的最小抑菌浓度[14]。配置20 480 μg/mL芽孢杆菌N-14菌体萃取物水溶液。首管芽孢杆菌N-14菌体萃取物浓度未加维氏气单胞菌E-12菌液前为20 480 μg/mL,取初始稀释液0.5 mL放在9支装有0.5 mL LB肉汤的无菌试管中,依次进行9次倍半稀释,最后一管弃0.5 mL。同时以0.5 mL LB肉汤为空白对照,这11支管最后分别加入0.5 mL制备好的维氏气单胞菌E-12菌液(1.5×108 cfu/mL),使各管芽孢杆菌N-14粗制发酵液的终浓度分别为10 240、2 560、1 280、640、320、160、80、40、20、10、0 μg/mL。置于摇床中30℃、150 r/min震荡培养24 h,观察各管菌体的生长情况,若前一管菌未生长而后一管有生长,则前者管中所对应的药物浓度即为该溶液对该菌的最小抑菌浓度。
1.3.6 菌株种属鉴定
参考《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》及《海洋新菌的分类与鉴定方法》对菌株进行初步鉴定[15-16]。采用平板划线法,将抑菌活性明显的菌株进行活化并提取基因组DNA,然后以真菌的ITS4、ITS5或细菌的16S rDNA的引物进行PCR扩增,所得产物委托上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司进行测序。测序所得基因序列在NCBI上进行Blast比对,并根据比对结果,选取近缘参考序列,通过Mega 7.0软件采用ClustalW进行比对,并采用邻接法(Neighbour-joining)构建系统树,选用Kimura 2-parameter 替代模型,自举(Bootstrap)分析次数为1 000。根据Blast和进化树分析结果确定该未知菌的种或属的分类地位。
2 结果与分析
2.1 各海洋菌株对各指示病原菌抑菌谱的测定与种属鉴定
滤纸片扩散法筛选结果显示,74株海洋菌株中,有28株海洋菌株(编号N-1~N-28)对各指示病原菌具有不同程度的拮抗活性。28株海洋菌株对各指示病原菌的抑菌谱测定结果如表1所示。由表可以看出,N-3、N-4、N-5、N-10、N-12、N-13、N-20、N-21、N-22对鳗鲡爱德华氏菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌、嗜水气单胞菌、维氏气单胞菌、副溶血弧菌、溶藻弧菌、哈维氏弧菌、大肠杆菌、鸡白痢沙门氏菌9种指示病原菌均具有明显的抑菌作用。基于16S rDNA分析的细菌种属初步鉴定发现,这9株微生物均为真菌,N-3为曲霉属菌(Aspergillus sp.);N-4为赭霉属菌(Ochroconis sp.);N-5为Roussoella sp.;N-10为Hortaea sp.;N-12和N-20均为翅孢壳霉属菌(Emericellopsis sp.);N-13为Pseudocosmospora sp.;N-21和N-22均为囊担菌属菌(Cystobasidium sp.)。
表1 海洋菌株对各指示病原菌抑菌谱测定结果
Tab.1
| 编号 Number | 菌属 Genus | A-01 | A-02 | A-03 | A-11 | A-12 | A-13 | B-01 | B-02 | B-03 | B-04 | B-05 | B-06 | B-07 | B-08 | B-11 | B-21 | C-01 | C-02 | C-03 | D-01 | D-02 | E-01 | E-02 | E-03 | E-04 | E-11 | E-12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-1 | Cystobasidium | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| N-2 | Hortaea | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-3 | Aspergillus | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| N-4 | Ochroconis | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | ++ | ++ | + | + | +++ | ++ | - | + | ++ | + | +++ |
| N-5 | Roussoella | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | - | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| N-6 | Alfaria | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| N-7 | Alfaria | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | - | + | + | - | + |
| N-8 | Emericellopsis | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | - | - | + | - | + |
| N-9 | Acremoyces | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-10 | Hortaea | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| N-11 | Streptomyces | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-12 | Emericellopsis | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | - | ++ | ++ | - | +++ |
| N-13 | Pseudocosmospora | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | ++ | +++ | + | +++ |
| N-14 | Bacillus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | + | ++ | - | ++ |
| N-15 | Beauveria | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| N-16 | Alfaria | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-17 | Streptomyces | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | ++ | ++ | - | ++ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-18 | Acremoyces | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-19 | Penicillium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | ++ | + | - | ++ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-20 | Emericellopsis | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | ++ | ++ | - | +++ |
| N-21 | Cystobasidium | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | ++ | ++ | - | +++ |
| N-22 | Cystobasidium | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | ++ | +++ | - | +++ |
| N-23 | Phaeophieospora | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | + |
| N-24 | Cystobasidium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | ++ | - | - | + | - | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | - | + | + | - | + |
| N-25 | Acremonium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| N-26 | Hortaea | ++ | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | - | + | ++ | - | + |
| N-27 | Trichosporon | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N-28 | Trichosporon | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | ++ | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
注:-不敏感(无抑菌圈);+低敏(抑菌圈7~10 mm);++中敏(抑菌圈10~15 mm);+++高敏(抑菌圈>15 mm)。
Notes:-indicated insensitivity (no bacteriostatic circle);+indicated low sensitivity (bacteriostatic circle 7~10 mm);++indicated moderately sensitive (bacteriostatic circle 10~15 mm);+++indicated high sensitivity (bacteriostatic circle>15 mm).
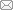
此外,N-11和N-17仅对大肠杆菌或鸡白痢沙门氏菌有抑菌活性,其种属鉴定为一种放线菌(Streptomyces sp.)。而N-14除了对大肠杆菌和鸡白痢沙门氏菌外,对嗜水气单胞菌和维氏气单胞菌也有明显的抑菌活性。菌株N-14根据16S rDNA的基因序列进行Blast比对并绘制进化树(图1),结果表明其与暹罗芽孢杆菌(Bacillus siamensis) (ON248947)和枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis) (HQ317166)的相似性最大(均大于99.8%),可以确定该菌株为芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus),但确定到种的分类地位还需要进一步的生理生化和其他管家基因的鉴定。
图1
图1
芽孢杆菌N-14基于16S rDNA序列的进化树分析
Fig.1
Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus sp. N-14 base on 16S rDNA analysis
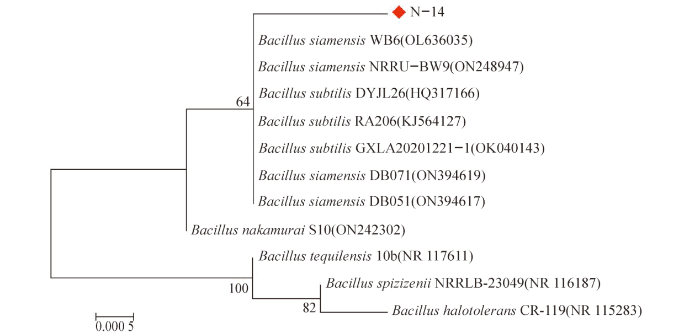
2.2 指示病原菌属对 9种海洋真菌的敏感程度
用抑菌圈的平均直径来表示各指示病原菌属对9种海洋真菌菌属的敏感程度,经One-way ANOVA和Tukey's多重比较统计分析(图2), 弧菌对曲霉属(Aspergillu)、Hortaea、Pseudocos mospora 的敏感程度相对较高,且与赭霉属(Ochroconis)、Roussoella、囊担菌属(Cystobasidium)有显著差异。另外,可以看出大肠杆菌对赭霉属的敏感程度最低。
图2
图2
各指示病原菌属对9种海洋真菌菌属的敏感程度
注:One-way ANOVA分析和Tukey’s多重比较分析, *P<0.05;**P<0.01;***P<0.001;****P<0.000 1。
Fig.2
The average diameter of the inhibition zone indicates the sensitivity of each indicator pathogen genus to 9 marine fungal genera
Notes:One-way ANOV analysis and tukey's multiple comparative analysis,*P<0.05;**P<0.01;***P<0.001;****P<0.000 1.
2.3 芽孢杆菌N-14对维氏气单胞菌E-12 的最小抑菌浓度
图 3
图 3
芽孢杆菌N-14菌体萃取物水溶液对维氏气单胞菌E-12的MIC
Fig.3
MIC of aqueous extract of N-14 bacilli against Aeromonas E-12
3 讨论
本研究通过滤纸片扩散法,从海洋环境中筛选出28株对特定病原菌具有拮抗作用的海洋菌株,经过鉴定发现9株具有明显抑菌作用的海洋菌株都是真菌,分别属于曲霉属、赭霉属、Roussoella、Hortaea、翅孢壳霉属、囊担菌属和Pseudocosmospora。目前已有许多学者对这7种菌属的抗菌活性及应用研究发表过报道。Monggoot S等研究发现Aspergillus sp. MFLUCC16-0845的主要抗菌成分是β-刺参素,可作为一种潜在的生物活性物质和植物防御激活剂来源 [17]。曲霉属真菌代谢产物丰富,在食品发酵、医药、农业生产等多个重要领域被广泛应用[18]。Phukhamsakda C等从猪苓铁线莲中分离出菌株Roussoella sp.(MFLUCC 17-2059),发现其次生代谢产物对金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)生物膜形成具有抑制作用[19]。Dunia A A F等发现嗜盐菌Hortaea sp.可以应用于蒽醌染料绿3的生物转化和解毒[20]。Eugene A R等从嗜碱菌Emericellopsis alkalina的培养基中分离到一种新型抗菌肽emericellipsin A,表现出很强的抗真菌作用和细胞毒活性,可用于开发抗真菌和抗肿瘤药物[21]。Santos R A等发现从不同水产养殖鱼类中分离出的芽孢杆菌能够通过群体猝灭来抑制鱼类病原体群体感应,达到抗细菌感染的作用,并且其中半数分离物能够有效地拮抗重要的鱼类病原体,包括嗜水气单胞菌、沙门氏菌、哈维氏弧菌、副溶血弧菌、爱德华氏菌和志贺氏菌(Shigella)等[22-23]。海洋菌株复杂多样,其抗菌活性物质及开发应用前景还有待进一步研究发现。
本研究还发现非真菌的N-14菌株,初步鉴定为芽孢杆菌属,其粗提物对气单胞菌、大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌都具有一定的抑菌作用。近年来,益生菌作为抗生素的安全替代品之一,以饲料 添加剂形式被广泛应用于水产养殖中。芽孢杆菌是一类革兰氏阳性化能异养菌,好氧或兼性厌氧,在自然界中分布广泛。芽孢杆菌能够形成芽孢,具有较强的耐酸、耐盐、耐高温及耐挤压等特性,其生物活性在恶劣环境中也不会降低。众多研究表明,芽孢杆菌在水产养殖中能降低水体氨氮亚盐水平,提高消化酶活性、抗氧化酶活性、免疫相关基因和应激相关基因的表达水平,增强鱼体对病原微生物的抵抗力等[24],已经成为水产养殖过程中常用的微生态制剂。芽孢杆菌保护鱼类免受致病菌侵害的机制包括产生抗菌活性物质、提高宿主免疫力、竞争黏附位点、营养物质和能量等,其中减少病原微生物是较为重要的益处之一[25]。不同鱼类对益生芽孢杆菌的最适需求量也不同,目前益生芽孢杆菌添加量与鱼体规格间还没有具体的规定,但总体来说,大规格鱼需要添加较多剂量的益生芽孢杆菌,小规格鱼对益生芽孢杆菌的剂量需求较少[26]。本研究的一个局限性在于仅通过N-14菌株的粗提物对气单胞菌进行了最小抑菌浓度的测试。N-14菌株在水产养殖中可能具有的较大的应用前景有待进一步的研究。
4 结论
本研究以东山兄弟屿的海绵、漳江口红树林的植株、土壤、螃蟹中分离提纯得到的74株海洋菌株为样品菌,以6株气单胞菌、6株爱德华氏菌、10株弧菌、2株沙门氏菌、3株大肠杆菌作为指示病原菌,利用滤纸片扩散法筛选测定菌株的抑菌谱,发现9株对大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌、爱德华氏菌、气单胞菌、副溶血弧菌、溶藻弧菌均具有明显抑制作用的海洋真菌,通过鉴定发现N-3属于曲霉属;N-4属于赭霉属;N-5属于Roussoella;N-10属于Hortaea;N-12和N-20均属于翅孢壳霉属;N-13属于Pseudocosmospora;N-21和N-22均属于囊担菌属。研究初步鉴定N-14菌株为芽孢杆菌属,对气单胞菌、沙门氏菌和大肠杆菌均具有一定的拮抗作用,其在水产养殖上的应用还有待进一步研究。本研究为深入探索海洋菌株抗菌活性物质及其应用前景提供了基础资料。
参考文献
一株史氏鲟源腐生葡萄球菌的分离鉴定及其基因组分析
[J].从周宁县某养殖场史氏鲟病灶样品中分离出1株多重耐药革兰氏阳性菌JY08,为了进一步研究其进化地位、耐药机制和潜在致病因子,采用形态学特征、16S rRNA基因序列、生理生化特征和系统发育树对其进行鉴定。结果显示,菌株JY08的形态特征和生理生化特性与腐生葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus saprophyticus)基本一致;16S rRNA基因序列与腐生葡萄球菌的相似度最高,为100%;系统发育树显示菌株JY08与腐生葡萄球菌腐生亚种(Staphylococcus saprophyticus subsp. saprophyticus ATCC 15305)聚为一支,结合全自动细菌鉴定仪生理生化特性鉴定结果和16S rRNA基因序列分析结果鉴定该菌株为腐生葡萄球菌。药敏试验结果表明,菌株JY08对β-内酰胺类、大环内酯类、磺胺类和林可霉素类等大类中的17种药物具有耐药性;对氨基糖苷类、喹诺酮类和氯霉素类等11种药物敏感;对多粘菌素B和呋喃唑酮2种药物中度敏感。耐药基因和毒力因子分析结果显示菌株JY08携带了10大类103个抗生素耐药基因和61种毒力因子123个相关毒力基因。本文研究结果为进一步评估该菌株潜在的具有感染能力的遗传特征提供科学数据,同时为该菌可能引起的疾病防控提供科学资料。
Antifouling activities of antagonistic marine bacterium Pseudomonas putida associated with an octopus
[J].
Isolation,identification and characterization of marine bacteria from the deep sea sediment of Bay of Bengal,India,and their antimicrobial and cytotoxicity potential
[J].
Isolation of marine Bacillus sp.with antagonistic and organic-substances-degrading activities and its potential application as a fish probiotic
[J].
地衣芽孢杆菌在水产养殖中的应用研究进展
[J].本文综合阐述了地衣芽孢杆菌特性、功能、作用机理以及在水产养殖中应用现状,并提出生产实践过程中存在问题和未来研究方向。地衣芽孢杆菌为革兰氏阳性兼性厌氧菌,对高温、酸性、胆盐和人工胃液有一定的耐受能力,是较具应用潜力的菌种之一;在水产养殖中具有调节肠道微生态平衡,提高机体免疫力,促进营养物质的消化吸收和净化养殖水环境的作用。科学使用地衣芽孢杆菌,可促进水产养殖业健康发展。
Chermesins A-D:meroterpenoids with a drimane-type spirosesquiterpene skeleton from the marine algal-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium chermesinum EN-480
[J].
The Emericellipsins A-E from an alkalophilic fungus Emericellopsis alkalina show potent activity against multidrug-resistant pathogenic fungi
[J].
Isolation of marine fungi Aspergillus sp.and its in vitro antifouling activity against marine bacteria
[J].
BSAC standardized disc susceptibilitytesting method
[J].For nearly a decade microbiologists have used the MIC breakpoints published in the BSAC Guide to Susceptibility Testing to interpret susceptibility. Historically, and unlike the rest of Europe, the UK and Ireland have used a comparative method of disc testing to interpret susceptibility rather than one based on a correlation between MIC and zone of inhibition. Although innovative when introduced in the 1970s, Stokes' comparative method has evolved ad hoc and it has become increasingly apparent that there is a need for a standardized method of disc testing that is correlated with BSAC MIC breakpoints. The method described here, like all other standardized methods of disc testing, cannot be adapted by the user, and interpretative criteria are only applicable if the method is adhered to fully. A major advantage of this approach to susceptibility testing is that data from several sources can be combined for surveillance of resistance, a task that has been made much easier by the introduction of this method and coincides with the availability of automated zone measuring devices. It is hoped that the method described here will provide the core document for standard operating procedures; however, changes will necessarily occur over time as the method is developed and refined.
应用微量稀释法测定消毒剂最小抑菌浓度方法的建立
[J].目的 建立测定消毒剂最小抑菌浓度(MIC)的微量稀释法。方法 采用微量稀释法,对部分消毒剂的MIC进行测定,并观察部分因素对测定结果的影响。结果 经对8株肺炎克雷伯菌临床分离株测试结果显示,三氯生有4株菌MIC值孵育48 h比24 h升高2倍,苯扎氯铵有1株菌MIC值升高2倍。继续对102株菌观察,西吡氯铵和醋酸氯己定也有MIC升高2倍的情况,只有十六烷基三甲基溴化铵MIC不发生变化。醋酸氯己定MIC基本不受所用肉汤培养基的影响,阳离子调节MH肉汤测定其余4种消毒剂MIC值为普通营养肉汤的2~4倍。利用OD600对无药物析出的醋酸氯己定和有药物析出的苯扎氯铵MIC进行判定和肉眼判读的结果完全一致。 结论 初步建立了以OD600来判定消毒剂MIC值的96孔板微量肉汤稀释方法。
Antibacterial potential of secondary metabolites produced by Aspergillus sp.,an endophyte of Mitrephora wangii
[J].
Biofilm inhibitory abscisic acid derivatives from the plant-associated dothideomycete fungus,Roussoella sp.
[J].Major proteins contained in dried giant grouper roe (GR) such as vitellogenin (from Epinephelus coioides; NCBI accession number: AAW29031.1), apolipoprotein A-1 precursor (from Epinephelus coioides; NCBI accession number: ACI01807.1) and apolipoprotein E (from Epinephelus bruneus; NCBI accession number: AEB31283.1) were characterized through compiled proteomics techniques (SDS-PAGE, in-gel digestion, mass spectrometry and on-line Mascot database analysis). These proteins were subjected to in silico analysis using BLAST and BIOPEP-UWM database. Sequence similarity search by BLAST revealed that the aligned vitellogenin sequences from Epinephelus coioides and Epinephelus lanceolatus share 70% identity, which indicates that the sequence sample has significant similarity with proteins in sequence databases. Moreover, prediction of potential bioactivities through BIOPEP-UWM database resulted in high numbers of peptides predominantly with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE-I) inhibitory activities. Pepsin (pH > 2) was predicted to be the most promising enzyme for the production of bioactive peptides from GR protein, which theoretically released 82 DPP-IV inhibitory peptides and 47 ACE-I inhibitory peptides. Overall, this work highlighted the potentiality of giant grouper roe as raw material for the generation of pharmaceutical products. Furthermore, the application of proteomics and in silico techniques provided rapid identification of proteins and useful prediction of its potential bioactivities.
Biotransformation and detoxification of antraquione dye green 3 using halophilic Hortaea sp.
[J].
A novel lipopeptaibol emericellipsin A with antimicrobial and antitumor activity produced by the extremophilic fungus Emericellopsis alkalina
[J].
Bacillus spp.inhibit Edwardsiella tarda quorum-sensing and fish infection
[J].The disruption of pathogen communication or quorum-sensing (QS) via quorum-quenching (QQ) molecules has been proposed as a promising strategy to fight bacterial infections. Bacillus spp. have recognizable biotechnology applications, namely as probiotic health-promoting agents or as a source of natural antimicrobial molecules, including QQ molecules. This study characterized the QQ potential of 200 Bacillus spp., isolated from the gut of different aquaculture fish species, to suppress fish pathogens QS. Approximately 12% of the tested Bacillus spp. fish isolates (FI). were able to interfere with synthetic QS molecules. Ten isolates were further selected as producers of extracellular QQ-molecules and their QQ capacity was evaluated against the QS of important aquaculture bacterial pathogens, namely Aeromonas spp., Vibrio spp., Photobacterium damselae, Edwardsiela tarda, and Shigella sonnei. The results revealed that A. veronii and E. tarda produce QS molecules that are detectable by the Chr. violaceum biosensor, and which were degraded when exposed to the extracellular extracts of three FI isolates. Moreover, the same isolates, identified as B. subtilis, B. vezelensis, and B. pumilus, significantly reduced the pathogenicity of E. tarda in zebrafish larvae, increasing its survival by 50%. Taken together, these results identified three Bacillus spp. capable of extracellularly quenching aquaculture pathogen communication, and thus become a promising source of bioactive molecules for use in the biocontrol of aquaculture bacterial diseases.
Isolation and characterization of fish-gut Bacillus spp.as source of natural antimicrobial compoundsto fight aquaculture bacterial diseases
[J].
Mechanisms and the role of probiotic Bacillus in mitigating fish pathogens in aquaculture
[J].